Medically Reviewed by:Scientific Advisory Board
Did you know that early detection of type 2 diabetes can lead to better health outcomes and reduce the risk of complications? Type 2 diabetes affects millions of people worldwide and can have serious consequences if left untreated. I
In this blog post, we’ll explore the signs and symptoms of type 2 diabetes, its causes and risk factors, and how to manage and prevent the condition. Let’s dive in and learn how to recognize the early signs of type 2 diabetes and take proactive steps to maintain our health.
A Summary of Type 2 Diabetes
-
Recognize the early signs of Type 2 diabetes, such as frequent urination and increased thirst.
-
Manage type 2 diabetes through lifestyle changes and interventions like a healthy diet, regular physical activity, stress management & medication.
-
Prevent type 2 diabetes by adopting healthy habits like eating balanced meals & exercising regularly to reduce risk factors.

Recognizing the Symptoms: 9 Signs of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes often develops gradually, making it crucial to recognize its early symptoms. These symptoms may include:
-
Frequent urination
-
Increased thirst
-
Constant hunger
-
Fatigue
Being aware of these signs can help you take necessary steps to manage the condition and prevent more severe complications.
Let’s explore these symptoms in detail.
Frequent Urination
Frequent urination is a common symptom of type 2 diabetes, caused by excess glucose in the blood. The kidneys work to filter the excess glucose, leading to an increased need to urinate, especially at night. High blood sugar levels can also contribute to other health problems, such as kidney failure and urinary tract infections.
It’s important to consult your doctor regularly if you experience frequent urination, as it may indicate the early stages of type 2 diabetes or other health issues. Timely diagnosis and management can help prevent complications and improve your overall well-being.
Increased Thirst
Increased thirst is another symptom of type 2 diabetes, often accompanying frequent urination. As the body loses more water through urination, dehydration occurs, triggering an increased need to drink fluids. This creates a vicious cycle, with frequent urination leading to dehydration and, in turn, increased thirst.
Staying aware of changes in your thirst levels and monitoring your fluid intake can help you identify potential signs of type 2 diabetes. If you notice a significant increase in thirst, consult your doctor to rule out possible health issues and receive proper guidance on managing your condition.
Constant Hunger
Persistent hunger, also known as polyphagia, can be another early sign of type 2 diabetes. When glucose is unable to enter the body’s cells due to insulin resistance, the cells are deprived of their primary energy source, leading to constant hunger. This excessive hunger can persist even after consuming an adequate amount of food.
Being mindful of changes in your appetite and addressing them through healthy eating habits can help control blood sugar levels and manage type 2 diabetes. Monitoring your blood sugar level is crucial, and consult your doctor if you experience constant hunger, as it may indicate an underlying health issue that requires professional guidance.
Fatigue
Fatigue is another common symptom of type 2 diabetes, resulting from insufficient sugar movement from the bloodstream to body cells. When the body does not produce enough insulin or when the body’s cells do not respond adequately to insulin, sugar is unable to move from the bloodstream into the cells, leading to an accumulation of sugar in the bloodstream and fatigue.
If you’re experiencing constant fatigue, it’s essential to consult your doctor to determine the underlying cause. Proper management of type 2 diabetes, including lifestyle changes and medication, can help improve energy levels and overall health.
Skin and Vision Changes
In addition to the symptoms mentioned above, type 2 diabetes can also cause noticeable skin and vision changes. Discolored, velvety patches of skin on the neck, armpit, or groin and impaired vision are among the signs that may indicate the presence of type 2 diabetes.
Let’s delve deeper into these changes and understand their connection to the condition.
Blurry Vision
Blurry vision is a symptom of type 2 diabetes, caused by an excess of sugar in the blood, which can damage the tiny blood vessels in the eyes. High blood sugar levels can result in blurry vision or swelling of the eye lens, making it difficult for the eye to focus properly.
If left untreated, these issues can lead to permanent vision loss. Regular eye check-ups are essential for people with type 2 diabetes, as early detection and treatment can help prevent more severe vision complications.
Patches of Darker Skin
Another skin change associated with type 2 diabetes is the appearance of darker, velvety patches of skin on the neck, armpit, or groin, known as acanthosis nigricans. These patches can be a sign of insulin resistance and may indicate the early stages of type 2 diabetes.
If you notice any changes in your skin, it’s crucial to consult your doctor for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Proper management of type 2 diabetes can help prevent further skin complications and improve your overall health.
Nerve Damage and Pain
High blood sugar levels can also lead to nerve damage, known as diabetic neuropathy, affecting various parts of the body. This damage can result in:
-
Pain
-
Numbness
-
Tingling sensations in the extremities
-
Reduced wound healing capabilities
Let’s take a closer look at these symptoms and their implications.
Tingling, Numbness, or Pain in Hands and Feet
Neuropathy caused by high blood sugar can lead to tingling, numbness, or pain in the hands and feet. This nerve damage occurs when blood sugar levels remain elevated for prolonged periods, damaging the nerves and impairing their function.
If you experience these sensations, it’s essential to consult your doctor to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment. Early detection and proper management of type 2 diabetes can help prevent further nerve damage and alleviate these symptoms.
Slow Wound Healing
Impaired poor blood circulation due to damaged blood vessels is another consequence of high blood sugar levels, leading to slow wound healing and an increased risk of infections. This reduced blood flow, which can be associated with high blood pressure, can make it difficult for the body to deliver oxygen, nutrients, and infection-fighting cells to the site of the wound, slowing down the healing process.
Maintaining proper blood sugar levels and taking care of your skin can help prevent slow wound healing and related complications. If you notice that a wound is taking longer than usual to heal, consult your doctor for guidance on appropriate treatment and care.
Infections and Complications
Type 2 diabetes can be associated with a range of diabetes complications, including:
-
Increased risk of heart disease
-
Stroke
-
Kidney disease
-
Nerve damage
-
Vision problems
For more information on managing these risks, consult the American Diabetes Association.
It’s essential to maintain a healthy lifestyle to reduce the risk of developing these infections and complications.
In this section, we’ll discuss some common infections and complications related to type 2 diabetes.
Itching and Yeast Infections
Itching and yeast infections are common complications associated with type 2 diabetes. High levels of glucose in the bloodstream can cause an overabundance of Candida, a fungus that can lead to itching and yeast infections. These infections can cause irritation, discharge, intense itchiness, burning, and redness in the affected area.
To reduce the likelihood of itching and yeast infections, practice good hygiene, wear loose-fitting clothing, and avoid douching. Additionally, individuals with type 2 diabetes should be mindful of their blood sugar levels and take necessary steps to keep them in a healthy range.
Oral Health Problems
Declining oral health is another complication associated with type 2 diabetes. People with type 2 diabetes are more likely to experience:
-
Gingivitis, which is an inflammation of the gums
-
Periodontal disease, which is an infection of the gums and bone that supports the teeth
-
Slow healing mouth sores, which can be indicative of the condition
Maintaining good oral hygiene and visiting your dentist regularly can help prevent oral health problems related to type 2 diabetes. If you experience any oral health issues, consult your dentist for appropriate treatment and recommendations on managing your diabetes.
Risk Factors and Causes
Understanding the risk factors and causes of type 2 diabetes can help you take proactive measures to prevent the condition. Being overweight, inactive, or having a family history of the disease are some of the risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes.
In this section, we’ll explore these risk factors in detail and discuss how they contribute to the development of the condition.
Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Managing type 2 diabetes involves a combination of:
-
Adopting a healthy diet
-
Engaging in regular physical activity
-
Managing stress
-
Taking medication as prescribed
-
Monitoring blood glucose levels
Incorporating the keyword “managing diabetes” into the text.
Managing type 2 diabetes, which is a part of managing diabetes, involves a combination of:
-
Adopting a healthy diet
-
Engaging in regular physical activity
-
Managing stress
-
Taking medication as prescribed
-
Monitoring blood glucose levels
These lifestyle changes and interventions can help lower blood sugar levels, control target blood sugar levels, and prevent complications.
If diet and exercise alone are not sufficient to regulate blood sugar levels, medications or insulin therapy may be prescribed. In this section, we’ll provide an overview of various management strategies for type 2 diabetes.
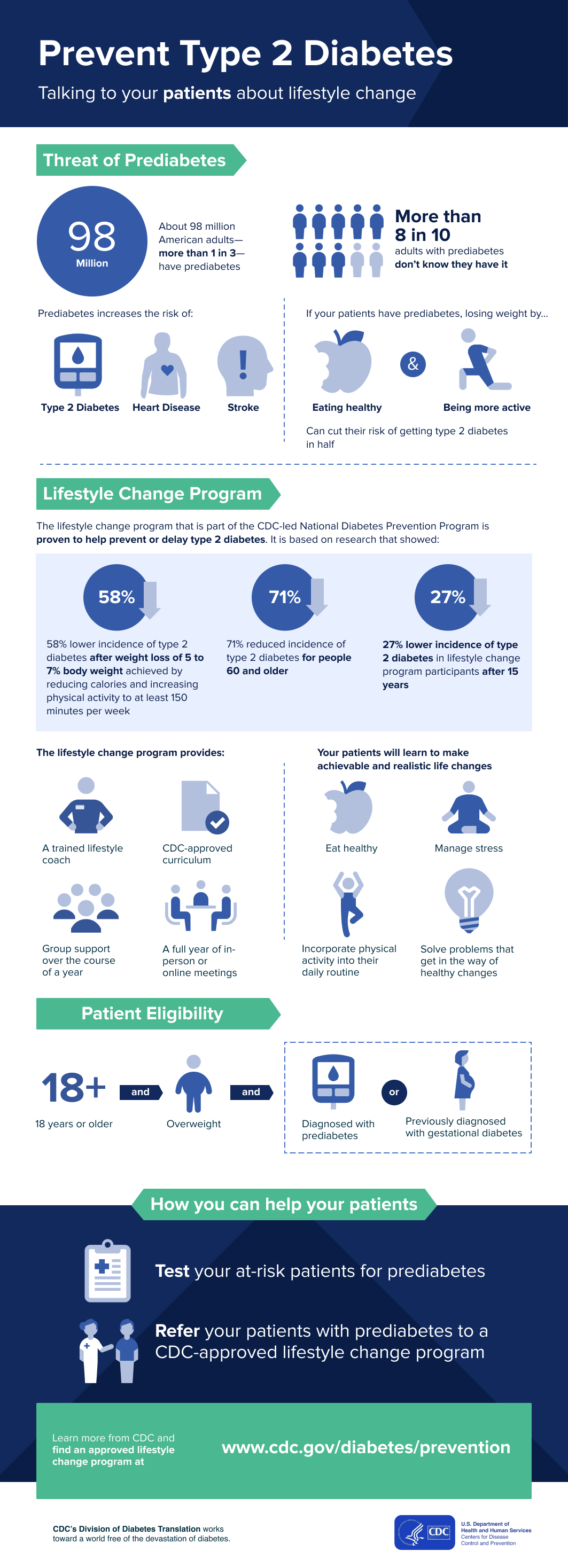
Prevention Strategies
Preventing type 2 diabetes starts with making healthy lifestyle choices, such as eating healthy foods. Maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress can help reduce the risk of developing the condition. By adopting these prevention strategies, you can improve your overall health and well-being, lowering your chances of developing type 2 diabetes and its related complications.
In this section, we’ll discuss the importance of these prevention strategies and how they can help you lead a healthier life.
Summary
In conclusion, recognizing the signs and symptoms of type 2 diabetes is crucial for early detection and effective management of the condition. By understanding the risk factors and causes, implementing prevention strategies, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, you can reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes and its associated complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the first warning signs of type 2 diabetes?
Common warning signs of type 2 diabetes include hyperglycemia, fatigue, increased thirst and urination, weight loss, blurred vision, and slow healing sores.
Regular screening is important in order to identify any early signs of diabetes.
What are 10 warning signs of type 2 diabetes?
Common warning signs of type 2 diabetes include frequent urination, excessive thirst, extreme hunger, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, vision changes, tingling and numbness in the hands or feet, dry skin, recurrent yeast infections, and slow-healing sores.
These symptoms can be caused by other medical conditions, so it is important to get a proper diagnosis from a doctor.
How can type 2 diabetes affect my vision?
High blood sugar levels from type 2 diabetes can cause blurry vision and swelling of the lens, leading to permanent vision loss if not managed.
What lifestyle changes can help manage type 2 diabetes?
Healthy eating, regular physical activity, and stress management are the cornerstones of effectively managing type 2 diabetes. By taking these lifestyle steps, you can control your blood sugar levels and avoid complications.
How is type 2 diabetes related to nerve damage and pain?
High blood sugar levels associated with type 2 diabetes can lead to nerve damage, resulting in pain, numbness, tingling, and reduced wound healing capabilities.
These symptoms can be debilitating and can significantly reduce quality of life. Treatment options include lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, as well as medications. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to find the best treatment plan for each individual.
References, Studies and Sources:
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/type-2-diabetes/symptoms-causes/syc-20351193
More About Circufiber.com and Healthcare disclaimer:
Always consult your physician before beginning any program. This general information is not intended to diagnose any medical condition or to replace your healthcare professional. If you experience any pain or difficulty, stop and consult your healthcare provider. Circufiber.com socks are clinically proven to improve micro-circulation in feet and lower extremities in people with Diabetes.
More Author Information:
Dr. Capozzi is a board-certified foot surgeon through the American Board of Foot and Ankle Surgery. He is a Diplomate of the American Academy of Wound Management and Fellow of the American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons. He completed a three-year residency program in Foot and Ankle Reconstructive Surgery at St. Francis Hospital & Medical Center in Hartford, CT in 2010. Dr. Capozzi is a board-certified Wound Specialist® granted by the American Academy of Wound Management. He is also board-certified in Foot Surgery through the American Board of Foot and Ankle Surgery.




