Diabetic ulcers, a common yet often overlooked complication of diabetes, can have a profound impact on a person’s quality of life. The importance of understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options cannot be overstated. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the multifaceted world of diabetic ulcers, exploring the significance of early detection, prevention strategies, and the critical role an interprofessional approach plays in effective management.
Short Summary
-
Diabetic Ulcers can lead to severe complications if not treated promptly and effectively.
-
Risk factors include uncontrolled blood glucose levels, duration of diabetes, poor circulation & nerve damage.
-
Early detection is key for successful management through proper foot care, regular check ups with healthcare professionals and appropriate treatment options such as wound care or antibiotics.
Understanding Diabetic Ulcers

People with diabetes are more likely to develop diabetic foot ulcers than others, due to inadequate glycemic control and the presence of other risk factors such as peripheral neuropathy, calluses on their feet or deformities. If left untreated, they can lead to non-traumatic lower extremity amputations. It is essential that people living with diabetes take good care of their feet by wearing comfortable footwear and paying attention to any signs of a developing ulcer in order for them not become serious complications.
To avoid damage, proper maintenance exercised over one’s foot health should always be taken seriously. Feeling okay isn’t enough when finding solutions since all these problems need special awareness met alongside addressing potential areas under pressure through well fitted shoes while inspecting regularly in case there exist susceptibilities linked directly to possible forming sores/wounds.
Poor circulation
Diabetic foot ulcers, which are commonly caused by poor circulation, can have a variety of underlying causes. These include the buildup of plaque in arteries and veins, blood clots, narrowing of the vessels from obesity or diabetes-related issues such as heart conditions and high cholesterol levels. Peripheral artery disease (PAD) may also be present due to raised blood pressure or varicose veins. These symptoms should all be checked for using an Ankle Brachial Index test (ABI). People who suffer with flat feet could also develop more frequent instances of diabetic foot ulcers because extra stress on certain areas means inflammation can occur easily.
Nerve damage (diabetic peripheral neuropathy)
Around 60 percent of individuals living with diabetes suffer from peripheral neuropathy due to nerve damage, leading to a reduced sensation and an elevated risk for injury or ulceration. One form of foot ulcer that is especially common among those who have diabetic peripheral neuropathy are neurotrophic ulcers which typically emerge on the pressure points such as toes and feet. They can be recognized by their tall borders. To the nearby tissues while having thin edges similar ‘punched out’.
Infection
Diabetic ulcers can be complicated by infections which may lead to additional tissue damage and impede the healing process. Cellulitis, myositis, abscesses, necrotizing fasciitis, septic arthritis and tendinitis as well as osteomyelitis have been linked to diabetic ulcers. If not addressed properly, these infections could potentially spread, causing severe health complications. To prevent this from occurring, treatments such as antibiotics for infection control should be taken up along with possible surgical interventions if needed.
Identifying Diabetic Foot Ulcers
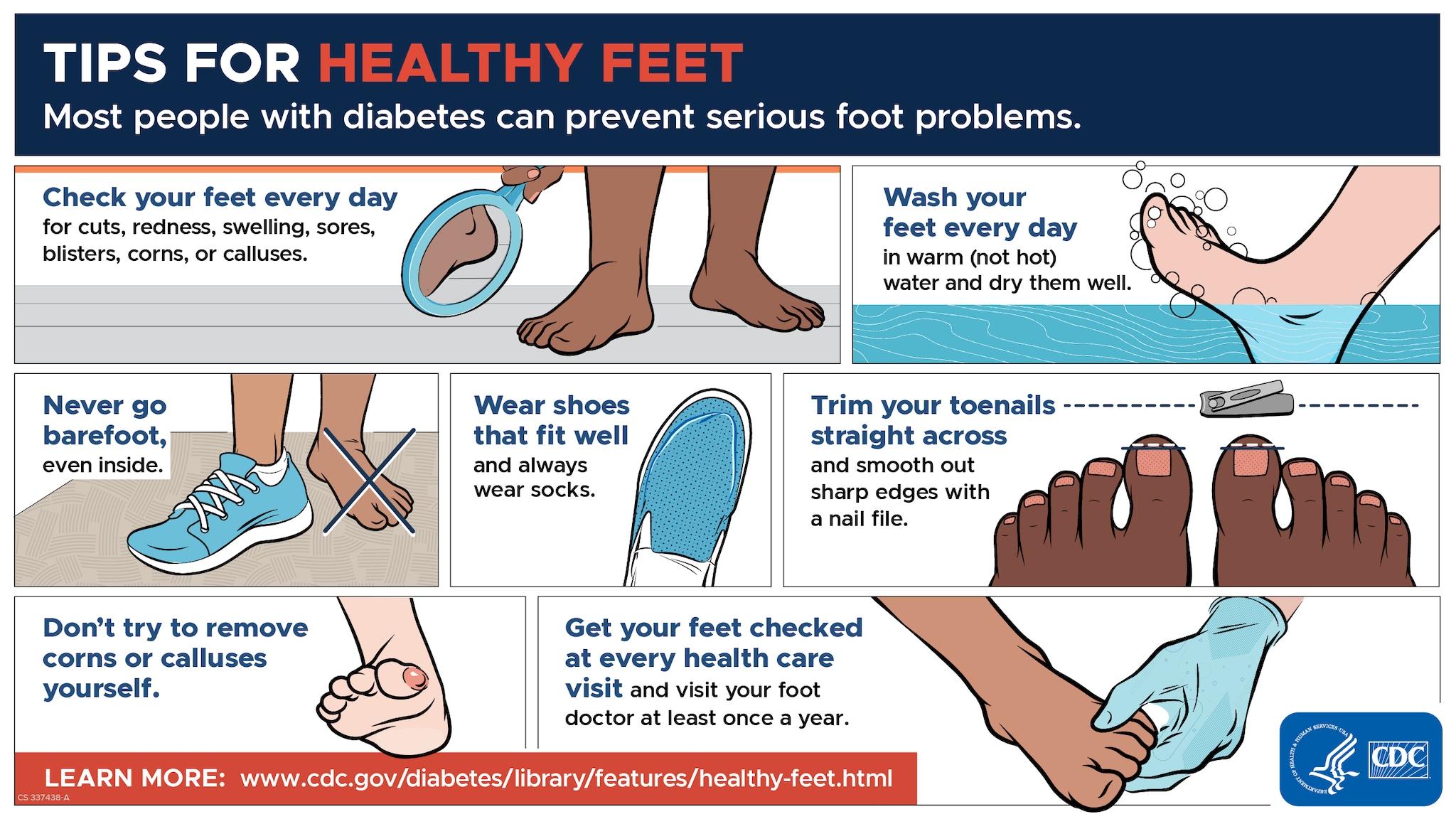
Properly diagnosing and treating diabetic foot ulcers as soon as they appear is essential. These types of wounds can be recognized by pain or discomfort, an unpleasant smell, noticeable redness or sores on the areas that bear weight such as heels, toes and around the metatarsal head. Diabetes-related blisters may also occur. To swelling and drainage from socks/shoes containing blood. Thick calluses with splitting skin along with cracked feet are other telltale signs of diabetes.
It is very important to get professional medical help if a foot ulcer develops so it can receive immediate attention for suitable treatment, leaving this too long will lead to complications down the line!
Visual appearance
Diabetics with neuropathy should routinely examine their feet and toes when dressing. A diabetic foot ulcer can be identified by certain alterations to the skin, such as modifications in color or odd shaped edges. The length and depth of an ulcer may increase until it reaches bone level if not taken care of properly. Regular inspection is recommended in order to avoid complications that could arise from this condition.
Pain or discomfort
When it comes to diabetic foot ulcers, the lack of pain can be attributed to decreased sensation in the feet due to neuropathy. This type of neuropathic pain, radicular discomfort and wound-related agony are typically linked with these types of sores.
When diagnosing or treating any form of diabetes related blisters on the extremities, care needs to be taken into account regarding neuronal issues that could lead to a loss of feeling around those areas affected by them.
Odor
The presence of a foul smell with diabetic ulcers is cause for alarm and should be addressed as soon as possible, since it may signal the onset of an infection that needs to be treated. Microorganisms such as bacteria are frequently the source behind this unpleasant odor. Immediate medical assistance is therefore essential.
Risk Factors for Diabetic Ulcers
Risk factors for diabetic foot ulcers include poor control of blood glucose levels, the length of time having diabetes and any other complications linked to it. Knowing these risks is fundamental in order to both reduce the chances of getting a diabetic foot ulcer as well as successfully managing them should they occur.
Early discovery and treatment are vitally important if we want minimize potential infection or amputation when dealing with this condition plus take care adequately of related issues pertaining to diabetic feet disease.
Uncontrolled blood glucose levels
Diabetic patients with uncontrolled blood glucose levels can be more vulnerable to developing ulcers. High sugar concentrations in the bloodstream may inflict nerve damage and impede proper circulation, impeding wound healing which boosts chances of forming sores particularly around feet area.
Peripheral neuropathy caused by diabetes is marked by inflammation and thickening of nerves resulting in sensations such as tingling or numbness being felt on the skin along with narrowed arteries that struggle to provide oxygen rich nutrients to areas like lower limbs.
Diabetes duration
Patients with diabetes should be aware of the risk factors associated with having the condition for an extended time period, as this can contribute to a greater chance of developing diabetic ulcers. Early diagnosis and treatment are key in order to help reduce potential complications that might otherwise arise from longer durations living with diabetes. Prompt attention could have positive implications for minimizing risks linked to diabetic ulcers.
Presence of other diabetes-related complications
Individuals with diabetes are more likely to develop diabetic ulcers due to having other health complications. These can include heart disease, chronic kidney disease and damage or dysfunction in the nerves, feet, mouth, eyesight, hearing ability and skin, as well as digestive problems or sexual difficulties. Foot issues such as a decreased blood flow that impairs wound healing capability along with nerve damage increase their probability of acquiring an ulcer even further.
Prevention Strategies for Diabetic Foot Ulcers
To prevent diabetic foot ulcers, people should take proper care of their feet and maintain good blood glucose levels. Regular visits to healthcare professionals are essential as they can detect any problems early on so that appropriate action is taken immediately. With the right preventive strategies in place, complications arising from these kinds of wounds may be avoided or at least minimized significantly.
Proper foot care
Adhering to the right kind of foot care is important for reducing one’s risk of diabetic foot ulcers. This includes inspecting feet daily, keeping them clean and dry, wearing shoes that fit properly, and never going barefoot when walking. As part of a regular routine practice, it is also recommended to wash any small cuts or blisters with soap and water before drying carefully. Applying moisturizing lotions can help preserve hydration levels. To use pumice stones or files on dead skin areas as well as antifungal creams for prevention against fungal infections which may develop. Ultimately your choice in footwear should be comfortable yet fitting, this plays an integral role towards achieving optimal diabetic foot health outcomes while guarding against potential injuries related to such conditions like ulceration.
Blood glucose management
For the prevention of diabetic foot ulcers, good management of blood glucose is vital. This includes keeping up a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity and adhering to any prescribed medication regimen.
By ensuring optimal levels of sugar in the bloodstream, it can help lessen nerve damage as well as poor circulation, which are both possible causes for developing foot ulcers related to diabetes.
Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals
It is of utmost importance that those suffering from diabetic foot ulcers make regular visits to healthcare professionals. This includes scheduling appointments with a doctor or podiatrist on a frequent basis for inspections and performing blood tests routinely to keep track of one’s glucose levels.
Consultations can help detect any evidence of impending ulcers at an early stage as well as gain advice on measures taken in the prevention thereof.
Treatment Options for Diabetic Ulcers
Monitoring diabetic ulcers regularly is essential to prevent complications. The choice of treatment for such wounds depends on the severity, location and presence or absence of infection or lack of blood flow (ischemia). Appropriate treatments could involve wound care with dressings as well as antibiotics in cases where there are infections present. Surgical interventions may also be considered. Early diagnosis and intervention will help avoid serious issues resulting from these types of lesions.
Wound care and dressings
The purpose of wound care and dressings is to protect the ulcer, stimulate healing, manage exudate flow, and reduce infection risk. It’s important that mild soap with water be used for cleaning followed by thorough drying before applying any type of dressing. Dressing options range from hydrocolloid to alginates. Foams or hydrogeal can also be considered depending on the condition of the area in need of care. The frequency at which a particular dressing needs changing may vary between 1-7 days, this will depend upon both what kind it is and how much progress has been made with recovering their ulcers!
Antibiotics for infections
For treating bacterial infections in diabetic ulcers, antibiotics may be prescribed depending on the type and severity of infection. Some appropriate antibiotics that can be utilized for this purpose include cephalexin, dicloxacillin, amoxicillin-clavulanate, clindamycin, vancomycin, as well as piperacillin/tazobactam. It is essential to keep a check on how the infection responds to these treatments. Changes might need to occur based on what works best against it.
Surgical interventions
In order to promote healing of serious and non-healing ulcers, surgical interventions may be needed. These can range from debridement (the removal of unhealthy tissue) to amputation (where a limb or part thereof is taken away), bone resection (partial eradication) as well as revascularization for restoring blood flow in the impacted region.
Vascular surgeons must work together with healthcare practitioners when deciding on which procedure would best suit an individual patient’s needs. All these measures are put forth so that maximum recovery can take place without complications arising due to such treatments carried out unnecessarily!
The Impact of Diabetic Ulcers on Quality of Life
Diabetic ulcers can have a substantial impact on an individual’s well-being, interfering with their mental health, physical capability and social life. Consequently, it is vital to focus not just on treating the wound but also all aspects of care that surround the person when managing diabetic wounds. This includes assessing potential root causes for those sores as part of providing overall comprehensive treatment.
Mental health considerations
Diabetic ulcers, when present chronically, can have an adverse effect on mental health such as depression and anxiety. It is imperative that the treatment for this condition includes considerations of the psychological aspects associated with them. The patients should be informed about potential repercussions so that appropriate resources and support may be offered to help manage those issues. It is also important to take into account other factors which could aggravate their state of mind while dealing with a chronic illness like diabetic ulceration.
Mobility challenges
Diabetic ulcers can lead to painful sensations and amputations, negatively impacting mobility. This discomfort reduces the ability to move comfortably and carries over into daily life as well. Consequently creating more challenges when it comes to conducting regular activities.
Social stigma and isolation
People with diabetes, particularly those who have diabetes mellitus, are already dealing with a range of issues. Consequently, the emergence of diabetic ulcers can cause difficulties due to potential social stigma and feelings of shame related to their appearance and odor that requires ongoing medical care. This may lead to isolated living conditions resulting in decreased quality of life for many individuals affected by these symptoms.
Importance of an Interprofessional Approach
The management of diabetic ulcers necessitates an interprofessional approach involving podiatrists, endocrinologists and vascular surgeons. This coordinated care is essential to properly diagnose, treat and prevent the development of these types of wounds in patients.
Podiatrists are responsible for examining foot health issues related to diabetes as well as giving preventive treatments. They also oversee the day-to-day management/care regarding any associated complications with this particular condition.
Podiatrists
People with diabetes must have good foot care to minimize the risks of complications. Podiatrists can assist in this effort by performing assessments for foot deformities, diagnosing and treating diabetic ulcers as well as providing wound treatment and dressings. They also provide ongoing education about proper prevention strategies when it comes to caring for feet.
Endocrinologists
Endocrinologists are well-positioned to oversee and manage blood glucose levels in people with diabetes as part of the process for treating ulcers. They provide guidance on dietary habits and lifestyle changes, can prescribe medications if necessary, and monitor closely those all important glucose readings.
Vascular surgeons
Vascular surgeons are experts in providing medical and surgical care to those with vascular conditions, both through medications or endovascular interventions and open surgery. With their specialist knowledge, they can diagnose the issue precisely and offer an effective treatment plan for even severe cases requiring revascularization procedures. Highly trained in this field, these professionals strive to ensure optimal results when treating patients affected by various types of vascular diseases.
Diabetic Ulcer Classification Systems
Diabetic ulcer classification systems, such as Wagner or University of Texas models, consider the depth of the wound along with infection and ischemia in determining how to treat a patient. This approach helps healthcare professionals weigh up each individual’s specific circumstances when deciding what form of treatment would be most beneficial for them. By utilizing these categorization techniques, clinicians can make well-informed decisions about which course to take regarding treating diabetic ulcers based on severity and characteristics.
Depth assessment
An assessment of the depth is necessary to ascertain how serious a diabetic ulcer is and decide on suitable treatment. Visual inspection, probing or even imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI can all be used for this purpose to evaluate any tissue damage and identify any infection present. This approach helps in determining an appropriate plan of action when managing these conditions.
Infection and ischemia evaluation
To identify potential infection and/or poor blood flow, it is essential to conduct the necessary diagnostic tests and examinations. These can include things such as blood tests, imaging exams or physical assessments that all serve to evaluate any indication of an underlying issue with either infection or lack of circulation. Through doing so, we will be able to ascertain what may have caused this abnormality in order for additional interventions to potentially take place if required.
Implications for treatment
Using the Wagner or University of Texas classification systems, healthcare practitioners can decide on an optimal treatment plan for their patient. This may be anything from wound care and dressings to antibiotics in case of infection to surgical procedures if needed.
Diabetic Ulcer Complications
Diabetic ulcers can be a serious health threat if left unchecked, as they may result in amputation, osteomyelitis and gangrene. Early intervention is paramount to avert these complications that might lead to deterioration of the patient’s quality of life. Appropriate management of diabetic ulcerations offers an opportunity for patients to obtain optimal care with improved outcomes.
Amputation
In some cases, amputation may be required when ulcers are severe or don’t heal, greatly affecting one’s quality of life. This is often the case with MLEA (major lower extremity amputations), including those done below the knee due to diabetic ulcer conditions.
Following an operation like this, physical therapy and occupational sessions will need to take place. To being fitted for a prosthesis.
Osteomyelitis
An infection of the bone, called osteomyelitis, can occur when diabetic ulcers are not treated or managed properly. Diagnostic methods for identifying this condition include a probe-to-bone test and imaging tests such as MRI scans. It is essential to detect it early in order to avoid any damage caused by the illness. To achieve that goal, various techniques may be utilized including prompt medical attention and treatment programs customized according to individual needs.
Gangrene
In extreme cases of diabetic ulcers, tissue death (gangrene) may occur and surgery could be necessary to treat it. Medicinal antibiotics may help clear the infection along with surgical removal of the dead areas as well as skin grafts which can replace damaged skin. In more serious situations, amputation might have to be an option for treatment.
Summary
By utilizing an interdisciplinary approach and preventive strategies, people living with diabetes can lessen the risk of developing diabetic ulcers. Early detection and correct management are essential in order to avoid complications as well as improve overall health and quality of life. Identifying potential causes, being mindful of associated risks factors such as poor glycemic control or lack of sensation in feet, plus comprehending available treatments all help when managing this condition properly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does diabetic ulcer look like?
Diabetic ulcers can become very serious, exposing bones and tendons. They are characterized by round lesions with redness at their borders and thickened skin in the vicinity of those lesions.
What are the first signs of a diabetic ulcer?
Diabetics should keep a close watch on their feet, as any changes could signal an ulcer. Signs to look out for include discoloration of the skin, swelling, tingling or numbness and potentially an open sore. The early detection of these symptoms can be key in ensuring efficient treatment is received before it develops into more serious complications.
Can diabetic ulcers go away?
Proper diagnosis and treatment are necessary to ensure that diabetic ulcers can be healed. Regular monitoring of the affected area, reducing pressure on the wound site, and specific therapies may need to be employed in order for a successful recovery. The period required will vary depending upon various aspects. It typically takes up to three months until full healing is achieved.
What are the typical underlying causes of diabetic foot ulcers?
Diabetic foot ulcers can be caused by a variety of factors, including poorly regulated blood sugar levels, calluses on the feet due to poor hygiene or incorrect footwear size/style, deformed feet that make it harder for shoes to fit properly and care not being taken with regards to daily maintenance. Peripheral neuropathy (nerve damage in certain areas) and insufficient circulation are also contributing causes of neuropathy.
How can I prevent the development of diabetic foot ulcers?
Taking proper care of your feet and keeping good control over blood glucose levels is essential to preventing diabetic foot ulcers.
To begin, it’s important that you keep up with a routine of daily washing using warm water and mild soap then moisturizing the skin afterwards. Regularly inspect your feet for any type of injury like cuts or blisters as this could be an indication of developing ulceration in diabetics’ feet, which can have serious consequences if left untreated by healthcare professionals!
References, Studies and Sources:
Ariani, Y., Tarigan, R. B., Pase, A. (2017). Foot Care and Risk Of Diabetic Foot In Patient With Type 2 Diabetes At H. Adam Malik Hospital Medan. Proceedings of the 1st Public Health International Conference (PHICo 2016). https://doi.org/10.2991/phico-16.2017.38
Pakaya, N., Kusnanto, K., Notobroto, H. B., Triyoga, R. S. (2021). Personal Agency Enhancing Model In Prevention Of Diabetic Foot Ulcer. Jurnal Aisyah : Jurnal Ilmu Kesehatan, (6). https://doi.org/10.30604/jika.v6is1.762
More About Circufiber.com and Healthcare disclaimer:
Always consult your physician before beginning any program. This general information is not intended to diagnose any medical condition or to replace your healthcare professional. If you experience any pain or difficulty, stop and consult your healthcare provider. Circufiber.com socks are clinically proven to improve micro-circulation in feet and lower extremities in people with Diabetes.
More Author Information:
Dr. Capozzi is a board-certified foot surgeon through the American Board of Foot and Ankle Surgery. He is a Diplomate of the American Academy of Wound Management and Fellow of the American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons. He completed a three-year residency program in Foot and Ankle Reconstructive Surgery at St. Francis Hospital & Medical Center in Hartford, CT in 2010. Dr. Capozzi is a board-certified Wound Specialist® granted by the American Academy of Wound Management. He is also board-certified in Foot Surgery through the American Board of Foot and Ankle Surgery.




